Unlock ESG Ethical & Responsible Investing
Understanding ESG Investing: More Than Just a Trend
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) investing isn’t just a fleeting fad; it’s a rapidly evolving approach to investing that considers a company’s impact on the world alongside its financial performance. It’s about recognizing that a company’s long-term success isn’t solely determined by its profit margins, but also by its commitment to environmental sustainability, its treatment of employees and stakeholders, and its adherence to strong governance principles. Investors are increasingly realizing that these factors are intrinsically linked to financial resilience and long-term value creation.
The Environmental Pillar: Protecting Our Planet
The ‘E’ in ESG stands for Environmental. This aspect focuses on a company’s impact on the environment, considering factors like its carbon footprint, water usage, waste management, and commitment to renewable energy. Companies with strong environmental practices are often better positioned to navigate the transition to a low-carbon economy and avoid potential regulatory penalties. Investors are increasingly demanding transparency and accountability from companies regarding their environmental performance, leading to a surge in the demand for sustainable and environmentally conscious investments.

The Social Pillar: People Matter
The ‘S’ represents Social factors, which encompass a company’s relationships with its employees, customers, suppliers, and the wider community. This includes aspects like labor standards, diversity and inclusion, human rights, data privacy, and product safety. Companies that treat their employees fairly, foster diverse and inclusive work environments, and prioritize ethical sourcing are generally seen as more resilient and better positioned for long-term success. Investors are increasingly recognizing the importance of social responsibility in creating a more equitable and just society.
The Governance Pillar: Transparency and Accountability
Governance (‘G’) focuses on a company’s leadership, executive pay, audit and risk management practices, and shareholder rights. Strong corporate governance ensures transparency, accountability, and ethical decision-making. Companies with robust governance structures tend to be less prone to scandals and legal issues, which can negatively impact their financial performance. Investors prioritize companies with strong governance structures as they demonstrate a commitment to responsible management and long-term value creation.
How ESG Investing Benefits Investors
Integrating ESG factors into investment decisions can lead to various benefits for investors. Studies have shown that companies with strong ESG profiles often outperform their counterparts over the long term. This is because companies with a commitment to sustainability, social responsibility, and good governance tend to be more resilient, innovative, and better able to manage risks. Moreover, ESG investing aligns investments with personal values, offering a sense of purpose beyond financial returns.
Identifying ESG-Focused Investments
Finding ESG-focused investments is becoming increasingly easier. Many investment firms now offer dedicated ESG funds and portfolios. However, it’s essential to do your research and understand the specific ESG criteria used by different investment managers. Some funds may focus on specific ESG themes, such as renewable energy or sustainable agriculture, while others may adopt a broader, integrated approach. Look for funds with transparent methodologies and clear reporting on their ESG performance.
Navigating the Complexity of ESG Ratings and Data
The ESG landscape is evolving rapidly, and the data used to assess a company’s ESG performance can vary significantly across different providers. This can make it challenging to compare companies and make informed investment decisions. It’s important to understand the methodologies used by different rating agencies and to consider multiple data sources when evaluating a company’s ESG performance. Remember that ESG ratings are just one piece of the puzzle and should be considered alongside traditional financial analysis.
The Future of ESG Investing: Continued Growth and Evolution
ESG investing is poised for continued growth in the coming years. As awareness of climate change and other environmental and social issues grows, more investors will demand greater transparency and accountability from companies. Regulatory changes are also likely to play a significant role in shaping the future of ESG investing. Investors can expect to see increased standardization of ESG data and reporting, as well as more stringent regulations related to environmental and social issues.
Beyond Financial Returns: The Impact of Ethical Investing
ESG investing is not just about achieving financial returns; it’s about aligning investments with personal values and contributing to a more sustainable and equitable future. By investing in companies that prioritize environmental sustainability, social responsibility, and strong governance, investors can have a positive impact on the world while also generating financial returns. It represents a shift towards a more holistic and responsible approach to investing, where financial performance is considered alongside broader societal and environmental impacts. Read also about ESG investing meaning.
Inclusive Growth A New Definition for Everyone
What Inclusive Growth Isn’t
Often, the term “inclusive growth” gets conflated with simply boosting overall economic growth. While a rising tide might lift some boats, it doesn’t automatically mean everyone benefits equally. Inclusive growth isn’t just about a bigger pie; it’s about ensuring everyone gets a fair slice. Focusing solely on GDP increases can exacerbate existing inequalities, leaving marginalized communities further behind. Genuine inclusive growth requires a more nuanced approach, one that directly addresses disparities in opportunity and access.
Beyond Economic Indicators: A Holistic View
Measuring inclusive growth goes beyond standard economic metrics like GDP per capita. We need to look at a broader spectrum of indicators to paint a complete picture. This includes things like income distribution, employment rates across different demographics, access to quality education and healthcare, environmental sustainability, and the reduction of social inequalities. A truly inclusive approach recognizes that economic well-being is intricately linked to social, environmental, and political factors. A healthy society, with robust social safety nets and equal opportunities, is the foundation upon which inclusive growth thrives.
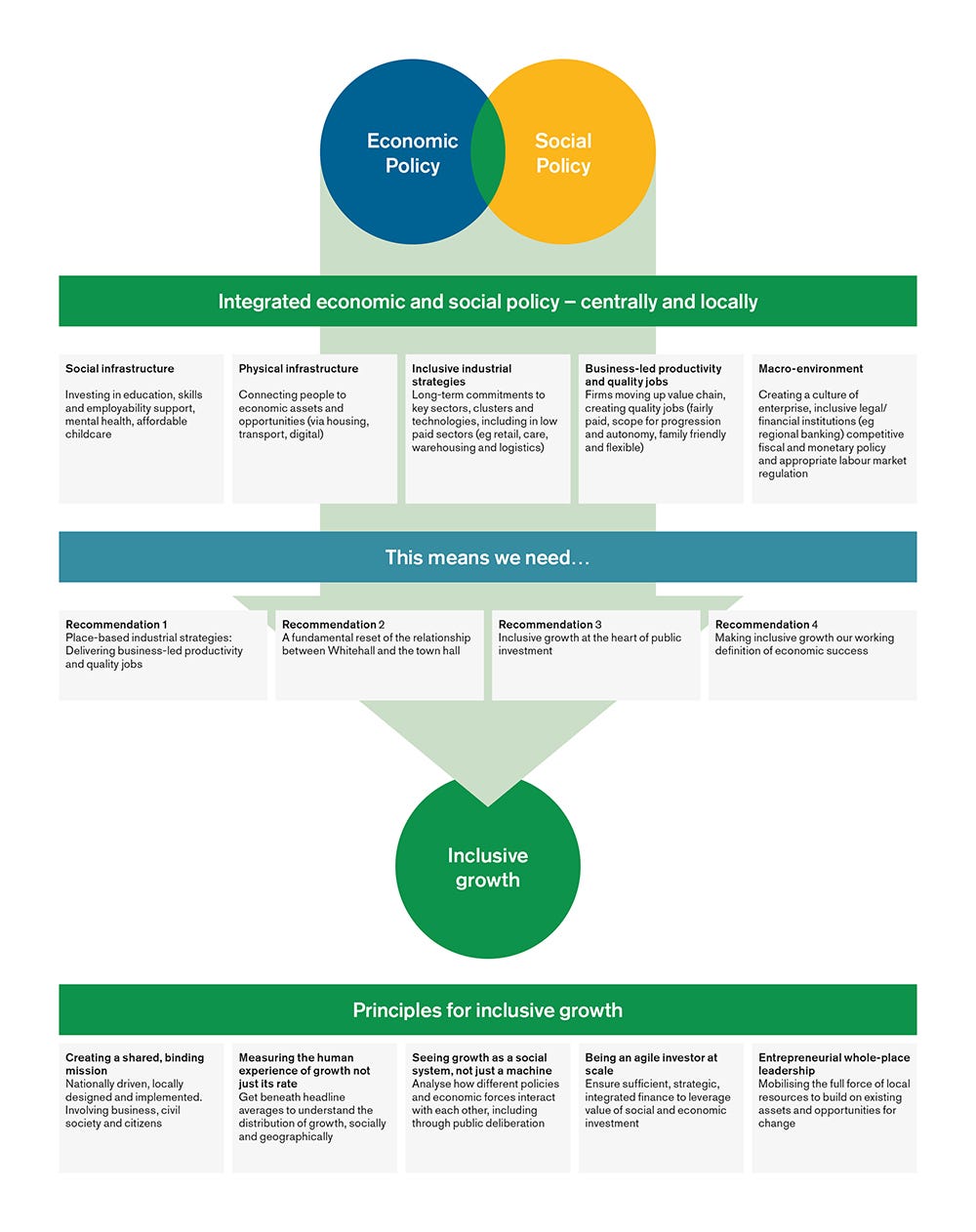
The Importance of Opportunity and Access
At the heart of inclusive growth lies the concept of equal opportunity. This means ensuring everyone has access to quality education, healthcare, decent employment, and financial services. Barriers based on gender, race, ethnicity, disability, or geographic location must be actively dismantled. This requires targeted interventions and policies that address the specific needs and challenges faced by marginalized groups. For example, initiatives promoting women’s economic empowerment, investing in infrastructure in underserved areas, and providing accessible technology are all crucial components.
The Role of Government and Policy
Governments play a vital role in fostering inclusive growth through strategic policymaking. This involves creating a level playing field, promoting competition, and investing in human capital. Progressive taxation policies can help redistribute wealth and reduce income inequality. Targeted social safety nets, including unemployment benefits, affordable housing programs, and food assistance, can protect vulnerable populations during economic downturns. Furthermore, investing in infrastructure, particularly in underserved communities, can stimulate local economies and create job opportunities.
The Private Sector’s Contribution
The private sector also has a critical role to play in achieving inclusive growth. Businesses can promote diversity and inclusion within their own organizations, creating equitable workplaces and opportunities for everyone. They can also invest in sustainable practices that benefit both the environment and local communities. Supporting local businesses and suppliers can stimulate economic activity in underserved areas. Corporate social responsibility initiatives that address social and environmental issues can contribute significantly to more inclusive outcomes. Ultimately, a collaborative effort between the public and private sectors is needed.
Measuring Progress and Accountability
Regularly monitoring and evaluating progress towards inclusive growth is essential. This requires robust data collection and analysis, using a comprehensive set of indicators. Transparent reporting on progress, including identifying areas where efforts are falling short, is critical. This data allows policymakers and businesses to adapt strategies and allocate resources effectively. Furthermore, holding stakeholders accountable for their contribution to inclusive growth is crucial for ensuring genuine progress. This includes promoting transparency and participation from all sectors of society.
Sustainable and Equitable Development
Inclusive growth isn’t just about short-term gains; it’s about building a sustainable and equitable future for everyone. This requires a long-term perspective that considers the environmental and social impacts of economic activity. Sustainable development practices, such as transitioning to renewable energy sources and promoting responsible resource management, are essential for ensuring that economic progress doesn’t come at the expense of the planet or future generations. Equitable access to resources and opportunities must be at the core of any sustainable development strategy.
Challenges and Opportunities
The path towards inclusive growth is not without its challenges. Addressing deeply entrenched inequalities requires sustained effort and political will. Overcoming resistance to change, ensuring equitable access to resources, and managing competing interests will require innovative solutions and collaborative partnerships. However, the opportunities are significant. By fostering inclusive growth, societies can build stronger, more resilient, and more equitable economies that benefit everyone, leading to a more just and prosperous future. Read also about inclusive economic development definition.
Green Investing Your Guide to a Sustainable Future
Understanding Green Investing
Green investing, also known as sustainable or responsible investing, involves putting your money into companies and projects that prioritize environmental sustainability and social responsibility. This isn’t just about feeling good; it’s about recognizing that environmental and social factors directly impact a company’s long-term success and profitability. A company that damages the environment or mistreats its workforce faces higher risks and potentially lower returns in the long run. Green investing aims to identify and support businesses actively mitigating these risks.
Different Approaches to Green Investing
There are several ways to incorporate green principles into your investment strategy. You could choose to invest directly in companies that are leaders in renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, or green technology. Alternatively, you could invest in funds or ETFs (exchange-traded funds) that specifically focus on environmentally and socially responsible companies. These funds often use screening criteria to exclude companies involved in activities like fossil fuels, deforestation, or weapons manufacturing, while prioritizing those with strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) ratings. Finally, you can engage in impact investing, where the primary goal is to generate positive social and environmental impact alongside financial returns.

Identifying Green Companies and Funds
Finding genuinely green investments requires careful research. Look for companies with publicly available sustainability reports, detailing their environmental performance, social initiatives, and governance practices. Independent rating agencies like MSCI and Sustainalytics provide ESG ratings that can help you assess a company’s commitment to sustainability. Similarly, when choosing funds, examine their investment strategies and portfolio holdings. Look for funds that clearly articulate their ESG criteria and regularly report on their impact. Don’t rely solely on marketing materials; delve deeper into the underlying data and methodologies.
The Role of ESG Factors
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors are at the heart of green investing. Environmental factors consider a company’s impact on the environment, including its carbon footprint, waste management, and resource consumption. Social factors encompass its treatment of employees, suppliers, and the communities where it operates. Governance refers to its corporate structure, ethical practices, and transparency. Analyzing these factors helps investors assess a company’s long-term sustainability and potential risks, allowing for more informed investment decisions. Strong ESG performance is often correlated with better financial performance.
Beyond the Bottom Line: Social Impact
Green investing isn’t solely about financial returns; it’s also about contributing to a more sustainable and equitable future. By supporting companies that prioritize environmental protection and social justice, you’re aligning your investments with your values. Many green investments directly contribute to positive social change, such as clean energy initiatives that reduce carbon emissions or sustainable agriculture practices that protect biodiversity. This positive impact can be both personally fulfilling and contribute to a broader shift towards a more sustainable global economy.
Risks and Considerations in Green Investing
While green investing offers significant potential, it’s essential to acknowledge the risks. The green sector is still developing, and some green companies might not be as financially stable as established companies in other sectors. Furthermore, the definition of “green” can be subjective, and “greenwashing” – the practice of falsely portraying a company as environmentally friendly – is a concern. Thorough due diligence and a well-diversified portfolio are crucial to mitigate these risks. It’s also important to remember that returns in green investments might not always be immediate or higher than traditional investments. The focus should be on the long-term, sustainable growth potential.
Getting Started with Green Investing
Begin by assessing your personal investment goals and risk tolerance. Consider your values and how they align with different investment approaches. If you’re unsure where to start, consult a financial advisor who specializes in sustainable investing. Many brokerage firms now offer a range of green investment options, including ESG funds and impact investing opportunities. Start small, gradually incorporating green investments into your portfolio, and continuously monitor your investments to ensure they align with your evolving goals and values. Remember, sustainable investing is a journey, not a destination.
The Future of Green Investing
Green investing is no longer a niche strategy; it’s becoming increasingly mainstream. As awareness of climate change and social issues grows, more investors are demanding transparency and accountability from companies. Government regulations and international agreements are also driving the shift towards a more sustainable economy. This trend is likely to continue, making green investing not just an ethical choice but also a smart long-term financial decision. The future of finance is undeniably intertwined with the future of the planet, making green investing a crucial component of responsible investing for years to come. Click here to learn about a sustainable investing strategy.
Shared Prosperity The Power of Inclusive Economies
Understanding Shared Prosperity
Shared prosperity isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a fundamental shift in how we think about economic growth. It moves beyond simply increasing the overall wealth of a nation and focuses instead on ensuring that the benefits of economic progress are broadly and equitably distributed across society. This means everyone, regardless of background, has the opportunity to participate in and benefit from economic growth, leading to a more just and stable society. It’s about creating an economy that works for everyone, not just the few at the top.
The Pillars of Inclusive Economies
Building an economy that fosters shared prosperity relies on several key pillars. Firstly, access to quality education and healthcare is paramount. A healthy and well-educated populace is a productive populace, capable of contributing meaningfully to the economy and improving their own lives. Secondly, decent work opportunities are crucial. This goes beyond simply having a job; it involves fair wages, safe working conditions, and opportunities for advancement. Thirdly, social safety nets are essential to provide a cushion for those facing hardship, ensuring that everyone has a basic standard of living. Finally, access to finance and entrepreneurship support allows individuals to start businesses, create jobs, and contribute to economic growth.

The Role of Government in Promoting Shared Prosperity
Governments play a vital role in creating the conditions necessary for shared prosperity. This involves implementing policies that promote inclusive growth, such as investing in education and infrastructure, creating a supportive regulatory environment for businesses, and strengthening social safety nets. Targeted interventions may be necessary to address specific challenges faced by marginalized communities, ensuring that everyone has a fair chance to succeed. Furthermore, effective governance and the reduction of corruption are vital to ensure that resources are used efficiently and equitably.
The Importance of Private Sector Engagement
While governments have a crucial role to play, the private sector is equally important in driving shared prosperity. Businesses have the power to create jobs, innovate, and contribute to economic growth. However, this needs to be done responsibly and inclusively. Businesses can contribute by adopting ethical business practices, investing in their employees, supporting local communities, and ensuring fair and sustainable supply chains. Collaboration between the public and private sectors is essential to achieve truly inclusive growth.
Measuring Progress Towards Shared Prosperity
Measuring shared prosperity requires a broader approach than simply looking at GDP growth. It necessitates tracking a range of indicators, including income inequality, poverty rates, access to education and healthcare, employment rates, and the overall well-being of the population. These indicators provide a more comprehensive picture of how economic progress is benefiting different segments of society and highlight areas where further action is needed. Transparency and data availability are crucial to track progress effectively.
Challenges and Obstacles to Shared Prosperity
The path towards shared prosperity is not without its challenges. High levels of income inequality, lack of access to resources, discrimination, and systemic barriers can all hinder progress. Rapid technological advancements can also exacerbate inequality if not managed carefully, potentially leading to job displacement and widening the gap between the skilled and unskilled workforce. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, involving collaboration across government, the private sector, and civil society.
The Long-Term Benefits of Shared Prosperity
Investing in shared prosperity isn’t just a matter of social justice; it’s also good economics. A more equitable distribution of wealth leads to greater social stability, reduced crime rates, and improved overall health outcomes. A more inclusive economy is also a more resilient economy, better equipped to withstand economic shocks and adapt to change. By fostering a society where everyone has the opportunity to thrive, we create a more prosperous and sustainable future for all.
Sustainable Development Goals and Shared Prosperity
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide a framework for achieving shared prosperity globally. Many of the SDGs, such as those focused on poverty eradication, quality education, decent work, reduced inequalities, and sustainable cities and communities, are directly linked to the principles of shared prosperity. By working towards these goals, countries can make significant progress in creating more inclusive and sustainable economies.
The Power of Collective Action
Ultimately, achieving shared prosperity requires a collective effort. Governments, businesses, civil society organizations, and individuals all have a role to play in creating an economy that works for everyone. By working together, sharing best practices, and fostering a culture of inclusivity, we can build a more just, equitable, and prosperous world for all. Read also about what is inclusive economic development.
Sustainable Investing Making Money & a Difference
What is Sustainable Investing?
Sustainable investing, also known as responsible investing or ESG (environmental, social, and governance) investing, goes beyond simply seeking financial returns. It integrates environmental, social, and governance factors into investment decisions. This means considering a company’s impact on the planet, its treatment of its workers and community, and its corporate governance practices alongside traditional financial metrics. It’s about aligning your investments with your values and contributing to a more sustainable future.
The Financial Case for Sustainable Investing
Many believe sustainable investing sacrifices profitability for ethical considerations. However, a growing body of research suggests that integrating ESG factors can actually enhance long-term financial performance. Companies with strong ESG profiles often demonstrate better risk management, innovation, and long-term resilience. They tend to attract and retain top talent, build stronger customer relationships, and face fewer regulatory and reputational risks. This translates into potentially higher returns and reduced volatility over time.
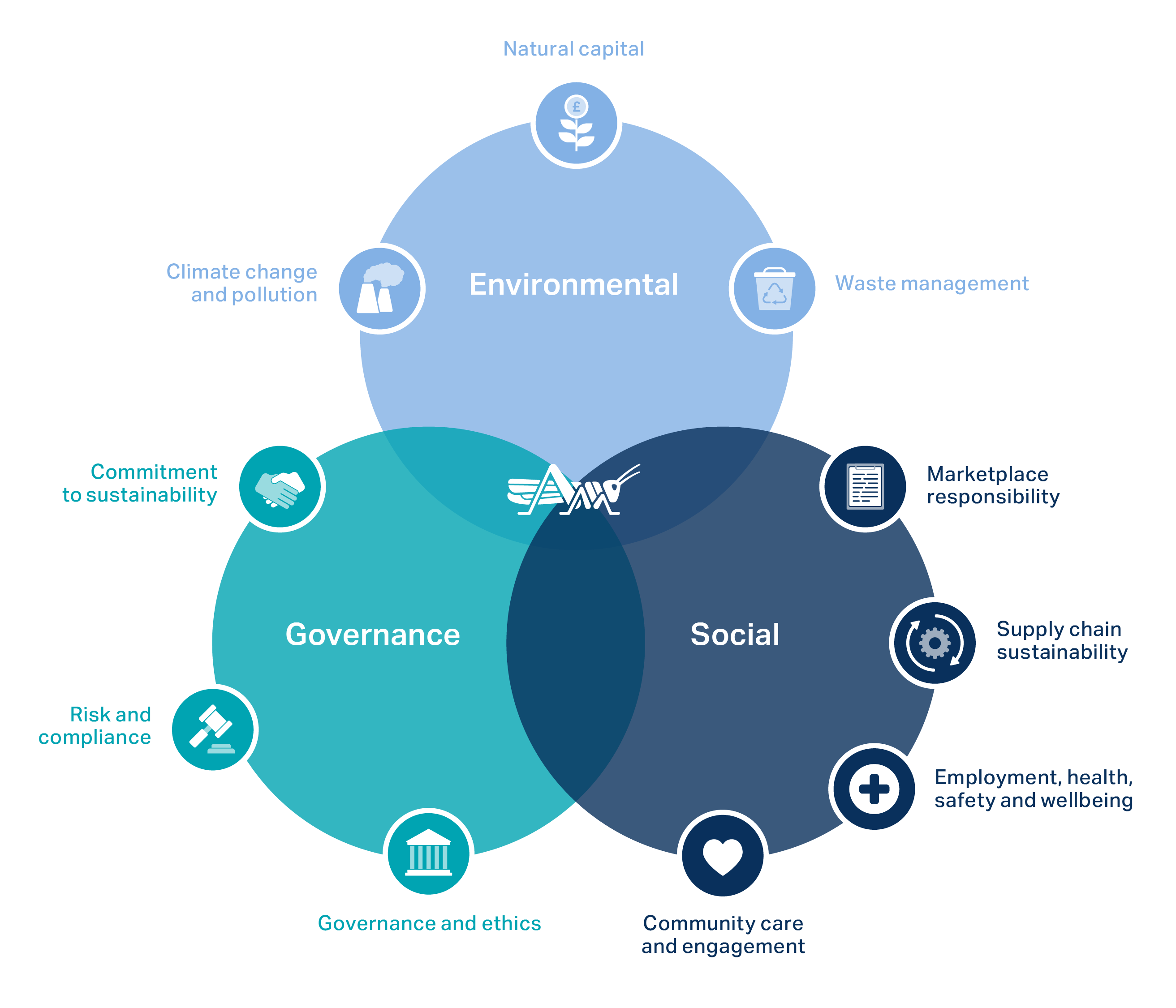
Identifying Sustainable Investments
Finding suitable sustainable investments can be easier than you think. Many asset managers now offer dedicated sustainable investment funds, ranging from equity and fixed-income portfolios to alternative investments. Look for funds that clearly outline their ESG criteria and investment strategies. Independent ratings agencies also provide ESG scores for companies, helping you assess their sustainability performance. It’s wise to engage with your financial advisor to identify investments aligned with your personal risk tolerance and ethical priorities.
Different Approaches to Sustainable Investing
There’s a spectrum of approaches within sustainable investing. Some investors focus on negative screening, avoiding companies involved in specific harmful activities like fossil fuels or tobacco. Others adopt positive screening, actively seeking out companies with strong ESG profiles. Impact investing aims to generate measurable social and environmental impact alongside financial returns. Finally, shareholder engagement involves actively engaging with companies to encourage them to adopt more sustainable practices.
Minimizing Greenwashing
It’s crucial to be wary of “greenwashing,” where companies exaggerate their sustainability credentials to attract investors. Do your due diligence. Scrutinize a company’s sustainability reports, looking for specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. Independent verification of ESG data is a strong indicator of authenticity. Look for companies that transparently disclose their environmental and social footprint, as well as their governance structure.
Beyond Financial Returns: The Social Impact
The benefits of sustainable investing extend beyond personal finance. By investing in companies committed to sustainability, you’re directly contributing to positive change. Your investment dollars can support the transition to a cleaner energy future, promote social equity, and improve corporate governance practices. This has a ripple effect, fostering innovation, creating jobs in emerging green sectors, and improving the overall well-being of communities and the planet.
Getting Started with Sustainable Investing
Starting your sustainable investing journey is simpler than you might imagine. You can begin by gradually shifting a portion of your portfolio towards sustainable investments. Many brokerage accounts offer tools and resources to screen for ESG-focused companies and funds. Talk to your financial advisor to incorporate sustainable investing into your overall financial plan, ensuring it aligns with your risk tolerance and financial goals. Remember, even small changes can make a big difference.
The Future of Sustainable Investing
The sustainable investing landscape is constantly evolving. Increasing regulatory pressure, growing consumer demand for ethical products and services, and a rising awareness of climate change are driving more capital towards sustainable investments. As the field matures, we can expect greater standardization of ESG data, more sophisticated investment strategies, and even more compelling evidence of the link between sustainability and financial performance. The future looks bright for those seeking both financial returns and positive social and environmental impact. Read also about ESG sustainable investing.




