Bitcoin Smart Contracts The Next Big Thing?
What are Bitcoin Smart Contracts?
Bitcoin, initially conceived as a decentralized digital currency, has limitations when it comes to complex functionalities. Unlike Ethereum, which is built from the ground up to support smart contracts, Bitcoin’s scripting language, Bitcoin Script, is relatively rudimentary. It’s designed for simple transactions, verifying ownership and transferring funds based on predetermined conditions. While not as versatile as Ethereum’s Solidity, Bitcoin’s smart contract capabilities are evolving, particularly with the advent of technologies like Taproot and the ongoing development of layer-two solutions.
Limitations of Bitcoin Script
Bitcoin Script’s simplicity is both its strength and its weakness. Its limited functionality means it can’t handle the complex logic and data structures found in more sophisticated smart contracts. This restricts the types of applications that can be built on Bitcoin. For example, complex decentralized applications (dApps) requiring multiple steps, intricate conditional logic, or extensive data storage are practically impossible to implement solely using Bitcoin Script. This limitation has pushed developers to explore alternative approaches.
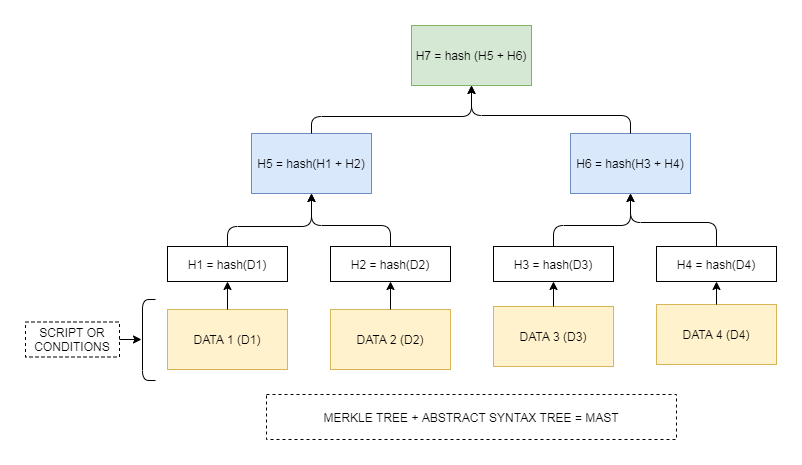
The Rise of Layer-2 Solutions
To overcome the limitations of Bitcoin Script, developers are increasingly exploring layer-two solutions. These are technologies built on top of Bitcoin that enhance its functionality without altering the underlying protocol. Examples include the Lightning Network and Liquid Network. These networks offer faster transaction speeds and lower fees, making them more suitable for applications that would be impractical on the main Bitcoin blockchain. While not directly smart contracts in the Ethereum sense, these layer-two solutions enable more complex functionalities through off-chain transactions and smart contract-like capabilities.
Taproot’s Impact on Bitcoin Smart Contracts
Taproot, a significant Bitcoin upgrade, significantly improves the efficiency and privacy of Bitcoin transactions. It does this by streamlining the scripting language, making it slightly more flexible and less computationally expensive. This isn’t a complete overhaul, but it paves the way for more sophisticated smart contracts. Taproot allows for more complex scripts to be executed with improved privacy, potentially enabling more nuanced and versatile applications on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Examples of Bitcoin Smart Contracts in Action
Despite limitations, Bitcoin smart contracts are already being used in various ways. Simple escrow services, where funds are held until specific conditions are met, are a common application. Other uses include decentralized finance (DeFi) projects that leverage layer-two solutions to create more complex financial instruments. These projects showcase the potential for more sophisticated applications even with Bitcoin’s current limitations. The development of decentralized exchanges (DEXs) on layer-two solutions is a testament to this growing capability.
The Future of Bitcoin Smart Contracts
The future of Bitcoin smart contracts is intertwined with ongoing developments in layer-two scaling solutions and potential future upgrades to the Bitcoin protocol itself. As layer-two technologies mature and become more widely adopted, the potential for complex applications built on Bitcoin will drastically increase. Future upgrades could potentially enhance Bitcoin Script, bringing it closer to the capabilities of smart contract platforms like Ethereum. However, the core philosophy of Bitcoin remains centered around its role as a secure and decentralized digital currency, which might limit the extent of smart contract development.
Comparing Bitcoin Smart Contracts to Ethereum Smart Contracts
It’s crucial to understand the fundamental difference between Bitcoin and Ethereum’s approach to smart contracts. Ethereum was designed with smart contracts at its core; its Turing-complete language, Solidity, allows for incredibly complex applications. Bitcoin, on the other hand, prioritizes security and decentralization, resulting in a less flexible scripting language. While Bitcoin’s smart contract capabilities are evolving, they are unlikely to ever match the breadth and depth of Ethereum’s smart contract ecosystem. The two platforms serve different purposes and cater to different development needs.
Security and Decentralization Considerations
Bitcoin’s primary strength lies in its robust security and high level of decentralization. This makes it an attractive platform for applications requiring a high degree of trust and reliability. While layer-two solutions can enhance functionality, they need to be carefully designed to maintain the security and decentralization properties of the underlying Bitcoin blockchain. Maintaining this balance is crucial for the long-term success of bitcoin smart contracts.
The Verdict: Next Big Thing or Niche Application?
Whether Bitcoin smart contracts become the “next big thing” is debatable. While they offer a secure and decentralized environment for specific applications, the inherent limitations of Bitcoin Script, compared to more robust platforms like Ethereum, will likely restrict their overall reach. However, the continuing evolution of layer-two solutions and potential future upgrades may significantly broaden their capabilities, making them a valuable tool for a growing subset of use cases within the broader crypto ecosystem. Their success hinges on balancing increased functionality with the core values of Bitcoin’s security and decentralization.
Crypto’s Secret Weapon Smart Contracts Explained
What are Smart Contracts?
Imagine a vending machine. You put in money, select your item, and the machine automatically dispenses your choice. No human intervention is needed. Smart contracts operate on a similar principle, but instead of snacks, they automate agreements and transactions on a blockchain. They are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. This code lives on a blockchain, making it transparent, secure, and tamper-proof.
The Power of Automation
The beauty of smart contracts lies in their automation. Once triggered by a predefined condition, they automatically execute the agreed-upon actions. This eliminates the need for intermediaries like lawyers or notaries, reducing costs, speeding up processes, and minimizing disputes. Consider a real estate transaction: a smart contract could automatically release funds to the seller once the property transfer is registered on the blockchain, eliminating the delays and risks associated with traditional escrow services.
Decentralization and Trust
Smart contracts run on decentralized networks, meaning they are not controlled by a single entity. This inherent decentralization builds trust among participants. Because the code is publicly viewable on the blockchain, anyone can audit it for vulnerabilities or verify its execution. This transparency fosters a higher level of trust than traditional contracts, where trust often relies on reputation and legal systems.
Beyond Simple Agreements: Complex Logic and Interactions
Smart contracts are not limited to simple agreements. They can incorporate complex logic and conditions, enabling sophisticated interactions. For example, a supply chain management system could use smart contracts to track goods, automatically trigger payments upon delivery verification, and even adjust pricing based on real-time market data. This level of automation and efficiency is transformative for businesses.
Security and Vulnerability Considerations
While smart contracts offer significant advantages, they are not without risks. Bugs in the code can be exploited, leading to financial losses or other undesirable outcomes. The “DAO hack” of 2016, where a vulnerability in a smart contract allowed for the theft of millions of dollars worth of cryptocurrency, serves as a stark reminder of the importance of rigorous code auditing and security best practices. Thorough testing and expert review are crucial before deploying any smart contract.
The Future of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are still a relatively young technology, but their potential applications are vast. Beyond finance and supply chain management, they are being explored in areas like digital identity, healthcare, voting systems, and intellectual property rights management. As the technology matures and becomes more widely adopted, we can expect to see even more innovative and impactful applications emerge, fundamentally changing how we interact and transact in the digital world. The possibilities are truly exciting, though careful consideration of security and legal implications will remain paramount.
Smart Contracts and DeFi
Decentralized finance (DeFi) is a prime example of smart contracts’ transformative power. DeFi applications rely heavily on smart contracts to create automated lending platforms, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), and other financial tools without the need for traditional financial institutions. This fosters financial inclusion and innovation by allowing individuals to access financial services globally without intermediaries.
Real-World Applications Beyond Finance
The utility of smart contracts extends far beyond the financial sector. Imagine a smart contract automating insurance payouts after a verified disaster, or a contract ensuring fair compensation for gig workers upon completion of tasks. These examples highlight the versatility and potential for positive social impact that smart contracts can offer across numerous industries. The future of smart contracts hinges on addressing security concerns and fostering wider adoption, but the potential is undeniable.
The Role of Developers and Auditors
The development and deployment of secure and reliable smart contracts require skilled professionals. Developers need expertise in blockchain technology and programming languages like Solidity, while security auditors play a critical role in identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities before a contract is launched. This collaborative effort is essential to ensure the responsible and widespread adoption of smart contracts and to prevent potential exploitation. Read also about crypto smart contracts.
Revolutionizing Business with Smart Contracts
What are Smart Contracts?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. They reside on a blockchain, a decentralized and immutable ledger, ensuring transparency and security. Unlike traditional contracts that rely on intermediaries and legal systems for enforcement, smart contracts automatically execute their terms when pre-defined conditions are met. This automation eliminates the need for trust in third parties and significantly speeds up processes.
Enhanced Security and Transparency
The decentralized nature of blockchain technology provides a significant boost to security. Smart contracts are tamper-proof, meaning that once deployed, their code cannot be altered without detection. This immutability creates a high level of trust and transparency, making them ideal for transactions requiring a high degree of accountability. All parties involved can easily access and verify the contract’s execution history on the public blockchain, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
Streamlining Supply Chain Management
Supply chains often involve numerous intermediaries, leading to inefficiencies, delays, and a lack of visibility. Smart contracts can revolutionize this by automating various stages, from order placement to payment processing and delivery confirmation. Each step is recorded on the blockchain, providing real-time tracking and improved traceability. This enhanced transparency helps to identify bottlenecks and improve overall efficiency, leading to reduced costs and faster delivery times.
Automating Payment Processes
Smart contracts can automate payments automatically upon fulfillment of certain conditions. For example, in a freelance contract, payment is released to the freelancer once the client confirms the completion of the work according to pre-defined specifications. This eliminates the need for manual intervention and reduces the risk of payment disputes. The automated payment process improves efficiency and builds trust between parties.
Dispute Resolution and Reduced Legal Costs
While not completely eliminating the need for legal intervention, smart contracts significantly reduce the likelihood of disputes. The clear and transparent nature of the contract, combined with its automatic execution, minimizes ambiguity and minimizes potential disagreements. Even if disputes arise, the readily available blockchain records provide strong evidence, streamlining the resolution process and potentially reducing legal costs. The unambiguous nature of the code itself can often serve as a sufficient mediator.
Improving Efficiency and Reducing Costs
The automation provided by smart contracts significantly reduces the time and resources required for managing contracts. Manual processes, such as verifying documents, chasing payments, and resolving disputes, are largely eliminated. This leads to significant cost savings for businesses, freeing up resources that can be allocated to other crucial aspects of the business. The reduced administrative overhead translates to a more efficient and agile operation.
Increased Trust and Collaboration
Smart contracts foster trust among parties involved in a transaction, even those who may not know each other personally. The transparency and immutability of the blockchain remove the need for intermediaries and build confidence. This increased trust can lead to greater collaboration and the development of new business relationships. This is particularly beneficial in cross-border transactions, where establishing trust can be challenging.
Challenges and Considerations
While offering immense potential, the adoption of smart contracts is not without challenges. The complexity of coding smart contracts requires specialized skills, and potential vulnerabilities in the code can be exploited. Legal frameworks surrounding smart contracts are still evolving, posing uncertainties for businesses. Furthermore, the reliance on technology means potential issues like network outages or technical glitches can disrupt contract execution.
Future of Smart Contracts in Business
Despite the challenges, the future of smart contracts in the business world looks bright. As blockchain technology matures and legal frameworks develop, we can expect wider adoption across various industries. The increasing sophistication of smart contract platforms, coupled with improved security measures, will address many of the current limitations. Smart contracts are poised to become a critical component of a more efficient, transparent, and secure business environment. Visit here to learn about smart contract development.


