Edge Computing Powering the Next Generation of Tech
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data. Instead of relying solely on centralized cloud servers, edge computing processes data at the “edge” of the network, closer to where it’s generated – think devices like smartphones, IoT sensors, or even autonomous vehicles. This proximity significantly reduces latency, improves bandwidth efficiency, and enhances real-time responsiveness.
Lower Latency for Real-Time Applications
One of the most compelling benefits of edge computing is its ability to drastically reduce latency. In applications requiring immediate responses, like autonomous driving, remote surgery, or real-time video analytics, the milliseconds saved by processing data locally can make all the difference. Imagine a self-driving car relying on cloud processing to react to an obstacle – the delay could be catastrophic. Edge computing eliminates this bottleneck, enabling near-instantaneous responses crucial for safety and efficiency.
Enhanced Bandwidth Efficiency and Reduced Costs
By processing data locally, edge computing significantly reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to a central cloud server. This translates to improved bandwidth efficiency, lowering network congestion and associated costs. For businesses dealing with massive datasets, like telecommunications companies or large-scale sensor networks, this can result in substantial savings in both infrastructure and operational expenses.
Improved Security and Data Privacy
Centralized cloud servers are attractive targets for cyberattacks. Edge computing, by distributing data processing, enhances security and strengthens data privacy. Sensitive data can be processed and stored closer to its origin, reducing the risk of data breaches during transmission. This is particularly important for industries with stringent data privacy regulations, such as healthcare and finance.
Powering the Internet of Things (IoT) Revolution
The proliferation of IoT devices is fueling the demand for edge computing. Millions of connected devices generate vast amounts of data, creating an overwhelming burden on centralized cloud infrastructure. Edge computing provides a scalable and efficient solution, enabling the seamless processing and analysis of data from these diverse sources, unlocking valuable insights and enabling smart city initiatives, predictive maintenance in manufacturing, and personalized healthcare experiences.
Enabling AI and Machine Learning at the Edge
Edge computing is a key enabler for bringing artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) closer to the data source. This allows for faster processing of data, real-time insights, and enables applications like intelligent video analytics, anomaly detection in industrial settings, and personalized recommendations without needing to constantly send data to the cloud. This on-device intelligence empowers smarter and more responsive systems.
Driving Innovation in Various Industries
The impact of edge computing spans across multiple industries. In manufacturing, it enables predictive maintenance and optimized production processes. In healthcare, it facilitates remote patient monitoring and real-time diagnostics. In transportation, it powers autonomous vehicles and smart traffic management systems. The versatility of edge computing makes it a transformative technology with wide-ranging applications.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its numerous benefits, edge computing presents some challenges. Managing and securing a distributed network of edge devices requires sophisticated infrastructure and security measures. The power consumption and computational capabilities of edge devices can also be limiting factors, especially in resource-constrained environments. Addressing these challenges is crucial for the widespread adoption of edge computing technology.
The Future of Edge Computing
The future of edge computing looks bright. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more powerful and efficient edge devices, improved network connectivity, and more sophisticated software tools to manage and analyze data at the edge. This will further expand the potential applications of edge computing and solidify its role as a cornerstone of the next generation of technological advancements. Learn more about edge computing solutions at scale here.
Edge Computing Simple, Powerful Solutions
What is Edge Computing?
Imagine a world where your data doesn’t have to travel miles to a distant server farm to be processed. That’s the promise of edge computing. Instead of relying on centralized cloud servers, edge computing processes data closer to its source – at the “edge” of the network. This could be on a device itself, a local server, or a small data center situated near where the data is being generated. Think of it like having a mini-data center strategically placed to handle local processing needs quickly and efficiently.
Why Choose Edge Computing?
The benefits are numerous and compelling. Reduced latency is a major win. When data processing happens locally, the delay between data creation and processing is significantly minimized. This is crucial for applications that require real-time responses, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and interactive gaming. Furthermore, edge computing enhances security by keeping sensitive data closer to its origin, reducing the risk of data breaches during transmission. Bandwidth consumption is also lessened, as less data needs to be sent over long distances.

Real-World Applications of Edge Computing
Edge computing isn’t just a futuristic concept; it’s already transforming various industries. In manufacturing, it enables predictive maintenance by analyzing sensor data from machinery to predict potential failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and saving costs. Smart cities leverage edge computing to optimize traffic flow, manage energy consumption, and improve public safety through real-time analysis of data from various sources like cameras and sensors. The healthcare sector benefits from faster processing of medical images, enabling quicker diagnoses and improved patient care. Even in retail, it allows for personalized shopping experiences through real-time inventory tracking and targeted promotions.
Simplified Deployment and Management
One might imagine edge computing solutions to be complex and challenging to implement, but that’s not always the case. Many modern edge computing platforms offer user-friendly interfaces and streamlined deployment processes. Cloud providers are also simplifying the integration of edge computing capabilities into their existing cloud services, making it easier for businesses to leverage the power of edge computing without needing extensive specialized knowledge. This accessible nature is a key driver of its widespread adoption.
Enhanced Security with Edge Computing
Security is paramount in today’s digital landscape, and edge computing offers a robust security advantage. By processing data closer to its source, the amount of sensitive information that needs to be transmitted across potentially vulnerable networks is reduced. This minimizes the risk of data breaches and interception, providing a more secure environment for sensitive applications. Combined with robust local security measures, edge computing contributes to a multi-layered security approach.
Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability
While initial investment might seem significant, the long-term cost-effectiveness of edge computing is considerable. Reduced latency translates to operational efficiency gains. Lower bandwidth usage leads to lower communication costs. Predictive maintenance and optimized resource allocation contribute to cost savings. Furthermore, edge computing solutions are designed to be scalable. As your needs grow, you can easily add more edge devices and resources without major disruptions to your existing infrastructure. This flexible scalability is vital for businesses aiming for future-proof technological solutions.
The Future of Edge Computing
Edge computing is rapidly evolving, with new advancements constantly emerging. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) at the edge is transforming how data is processed and analyzed, enabling more sophisticated applications and greater automation. The rise of 5G and other high-bandwidth, low-latency networks is further fueling the adoption of edge computing by providing the necessary infrastructure for seamless data transfer and real-time processing. The future of edge computing promises even more powerful and efficient solutions, transforming how we interact with technology and the world around us.
Choosing the Right Edge Computing Solution
Selecting the right edge computing solution depends on various factors, including your specific needs, budget, and technical expertise. There’s a wide range of options available, from simple, plug-and-play devices to complex, customized systems. Carefully assessing your requirements and seeking expert guidance can help you choose a solution that perfectly aligns with your business goals and delivers the desired results. Remember to consider factors like data volume, processing requirements, security needs, and scalability when making your decision. Read more about cloud edge computing solutions.
Edge Computing The Future is Closer Than You Think
What is Edge Computing?
Imagine a world where your smart devices don’t rely on distant servers to process information. That’s the promise of edge computing. Instead of sending data across vast networks to a central data center (the “cloud”), edge computing processes data closer to its source—at the “edge” of the network. This could be on your local device, a nearby server, or a small data center in your community. This proximity drastically reduces latency, improves bandwidth efficiency, and opens up possibilities for real-time applications previously impossible with cloud-centric architectures.
The Rise of Data and the Limitations of the Cloud
We’re drowning in data. The Internet of Things (IoT) is exploding, with billions of connected devices generating massive amounts of information every second. Relying solely on cloud computing to handle this data deluge presents several challenges. The sheer volume of data can overwhelm cloud infrastructure, leading to delays, bottlenecks, and increased costs. Furthermore, the distance data must travel to reach the cloud and back can introduce significant latency, making real-time applications impractical or impossible. Think self-driving cars, remote surgery, or sophisticated industrial automation—all these require immediate processing of data, which the cloud struggles to provide consistently.
Speed and Efficiency: The Core Benefits of Edge Computing
The most compelling advantage of edge computing is speed. Processing data locally or nearby dramatically reduces latency. This near-instantaneous processing opens doors to applications that depend on real-time responsiveness. Consider a factory floor where sensors monitor equipment performance. With edge computing, immediate analysis of sensor data can allow for proactive maintenance, preventing costly downtime. Similarly, in autonomous vehicles, quick processing of sensor data is crucial for safe and efficient navigation. The reduction in data transmission also enhances bandwidth efficiency, saving costs and improving overall network performance.
Enhanced Security and Data Privacy
Edge computing also offers significant security and privacy advantages. By keeping sensitive data closer to its source, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Instead of transmitting potentially vulnerable data across vast networks, it remains within a more controlled and secure environment. This is particularly important in industries like healthcare and finance, where data protection is paramount. The localized nature of edge computing also makes it easier to comply with data privacy regulations like GDPR, which require data to be processed within specific geographical regions.
Expanding Applications Across Industries
The applications of edge computing are expanding rapidly across a variety of industries. In manufacturing, edge computing enables predictive maintenance, optimizing production lines, and improving product quality. In healthcare, it facilitates real-time monitoring of patients’ vital signs and enables remote surgery. Smart cities are leveraging edge computing to manage traffic flow, optimize energy consumption, and enhance public safety. Retailers are using it to personalize the shopping experience and improve inventory management. The possibilities are seemingly endless, limited only by imagination and technological advancements.
Challenges and Considerations for Widespread Adoption
Despite its advantages, edge computing faces certain challenges. Deploying and managing distributed edge infrastructure can be complex and costly. Ensuring consistent security and data management across multiple edge locations requires robust security protocols and efficient management tools. The need for skilled personnel to manage and maintain these distributed systems is also a significant hurdle. However, as technology advances and the cost of edge devices decreases, these challenges are becoming less significant, paving the way for broader adoption.
The Future of Edge Computing: A Collaborative Ecosystem
The future of edge computing is likely to involve a collaborative ecosystem of players. This includes hardware manufacturers providing edge devices, software developers creating applications for the edge, telecom providers building robust edge networks, and cloud providers integrating edge computing with their cloud services. This collaboration will be crucial in driving innovation, addressing challenges, and unlocking the full potential of edge computing. We are only beginning to scratch the surface of what’s possible, and the next few years will undoubtedly witness a dramatic transformation in how we process and utilize data, driven by the transformative power of edge computing.
From Science Fiction to Everyday Reality
Edge computing is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s actively reshaping industries and influencing our daily lives. From the smart devices in our homes to the sophisticated systems powering autonomous vehicles, edge computing is silently yet powerfully improving efficiency, enhancing security, and unlocking new possibilities. As technology continues to evolve, edge computing’s influence will only grow, making it a pivotal force in the technological landscape of tomorrow, and indeed, today. Read also about edge computing solutions.
Edge Computing Powering the Future of Business
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation. Instead of relying solely on centralized cloud servers, edge computing processes data at the “edge” of the network, closer to devices like sensors, IoT gateways, and mobile devices. This proximity reduces latency, improves bandwidth efficiency, and enables real-time processing of data, creating opportunities for businesses across diverse sectors.
Reduced Latency and Improved Response Times
One of the most significant advantages of edge computing is its ability to drastically reduce latency. Imagine a manufacturing plant using sensors to monitor equipment performance. With cloud-based processing, data from these sensors needs to travel to a distant server, be processed, and then send instructions back. This back-and-forth can take valuable time, potentially leading to production delays or even equipment damage. Edge computing, however, processes this data locally, allowing for immediate responses and adjustments, significantly improving efficiency and minimizing downtime.
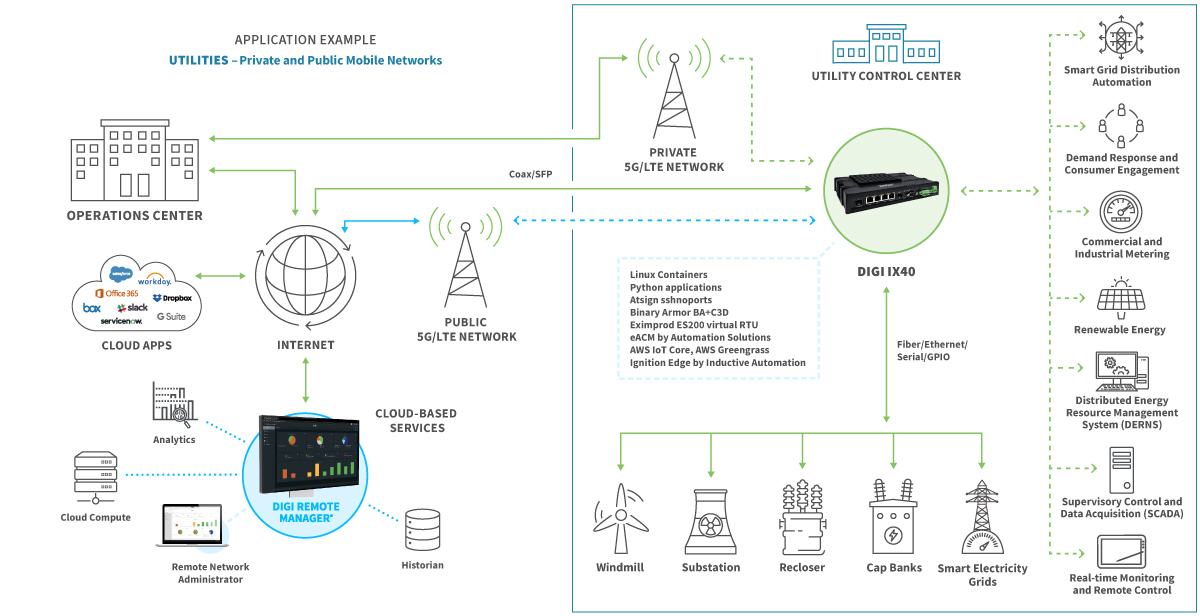
Enhanced Data Security and Privacy
Moving data processing closer to the source also enhances data security. Less data needs to travel across the network, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. This is especially important for businesses handling sensitive information like financial data, medical records, or personal customer details. Edge computing allows for local data encryption and processing, minimizing the potential impact of security vulnerabilities.
Enabling Real-Time Analytics and Decision Making
The ability to process data in real-time is transforming how businesses operate. With edge computing, organizations can gain immediate insights into their operations, allowing for faster decision-making. For example, a retail store can analyze customer traffic patterns in real-time using edge-enabled cameras and adjust staffing levels accordingly. This agility and responsiveness provide a significant competitive advantage in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Cost Savings and Improved Efficiency
While implementing an edge computing infrastructure might involve some upfront investment, the long-term cost savings can be substantial. By reducing the amount of data transmitted to the cloud, businesses can lower bandwidth costs and reduce their reliance on expensive cloud storage. The improved efficiency resulting from real-time analytics and reduced latency also translates into significant cost savings across various operational areas.
Scalability and Flexibility for Growing Businesses
Edge computing offers scalability and flexibility, making it an ideal solution for businesses of all sizes. As a business grows, its edge infrastructure can easily be expanded to accommodate increased data volumes and processing requirements. This scalability ensures that businesses can adapt to changing needs without significant disruption or costly overhauls. The modular nature of edge deployments also allows for tailored solutions to specific business needs, regardless of size or industry.
Powering Innovation in Various Industries
The applications of edge computing are vast and continue to expand across various industries. In manufacturing, it enables predictive maintenance and optimizes production processes. In healthcare, it facilitates remote patient monitoring and improves the speed and accuracy of diagnoses. In the transportation sector, it enhances autonomous driving capabilities and improves traffic management. The versatility of edge computing is fueling innovation and driving significant improvements in efficiency and productivity across a wide range of sectors.
Addressing the Challenges of Edge Computing
Despite its numerous advantages, edge computing also presents some challenges. Managing and maintaining a distributed network of edge devices can be complex, requiring robust management tools and skilled personnel. Ensuring data consistency and synchronization across multiple edge locations also requires careful planning and implementation. Addressing these challenges requires a strategic approach that balances the benefits of edge computing with the practical considerations of implementation and maintenance.
The Future of Edge Computing in Business
The future of edge computing in business is bright. As technology continues to advance and costs decrease, edge computing will become increasingly prevalent, empowering businesses to achieve greater efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) at the edge will further enhance the capabilities of edge computing, driving even more transformative changes across various industries. The power of edge computing to process data closer to the source is reshaping the business landscape, paving the way for a more connected, responsive, and efficient future. Click here to learn about enterprise edge computing solutions.



