Eco-Friendly Factories The Future of Making
The Growing Urgency for Sustainable Manufacturing
The impact of traditional manufacturing on the environment is undeniable. From resource depletion and pollution to carbon emissions and waste generation, the industry has long been a significant contributor to climate change and environmental degradation. As awareness of these issues grows, so does the pressure on manufacturers to adopt more sustainable practices. Consumers are increasingly demanding eco-friendly products, and governments are implementing stricter environmental regulations. This creates a compelling case for a shift towards eco-friendly factories, not just as a matter of corporate social responsibility, but as a matter of economic survival and long-term viability.
Renewable Energy: Powering the Green Factory
One of the most significant steps towards eco-friendly manufacturing is transitioning to renewable energy sources. Solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal energy can dramatically reduce a factory’s carbon footprint by eliminating reliance on fossil fuels. While the initial investment might be substantial, the long-term cost savings and environmental benefits make it a worthwhile endeavor. Furthermore, many governments offer incentives and subsidies to encourage the adoption of renewable energy technologies, making the transition more financially feasible for businesses.
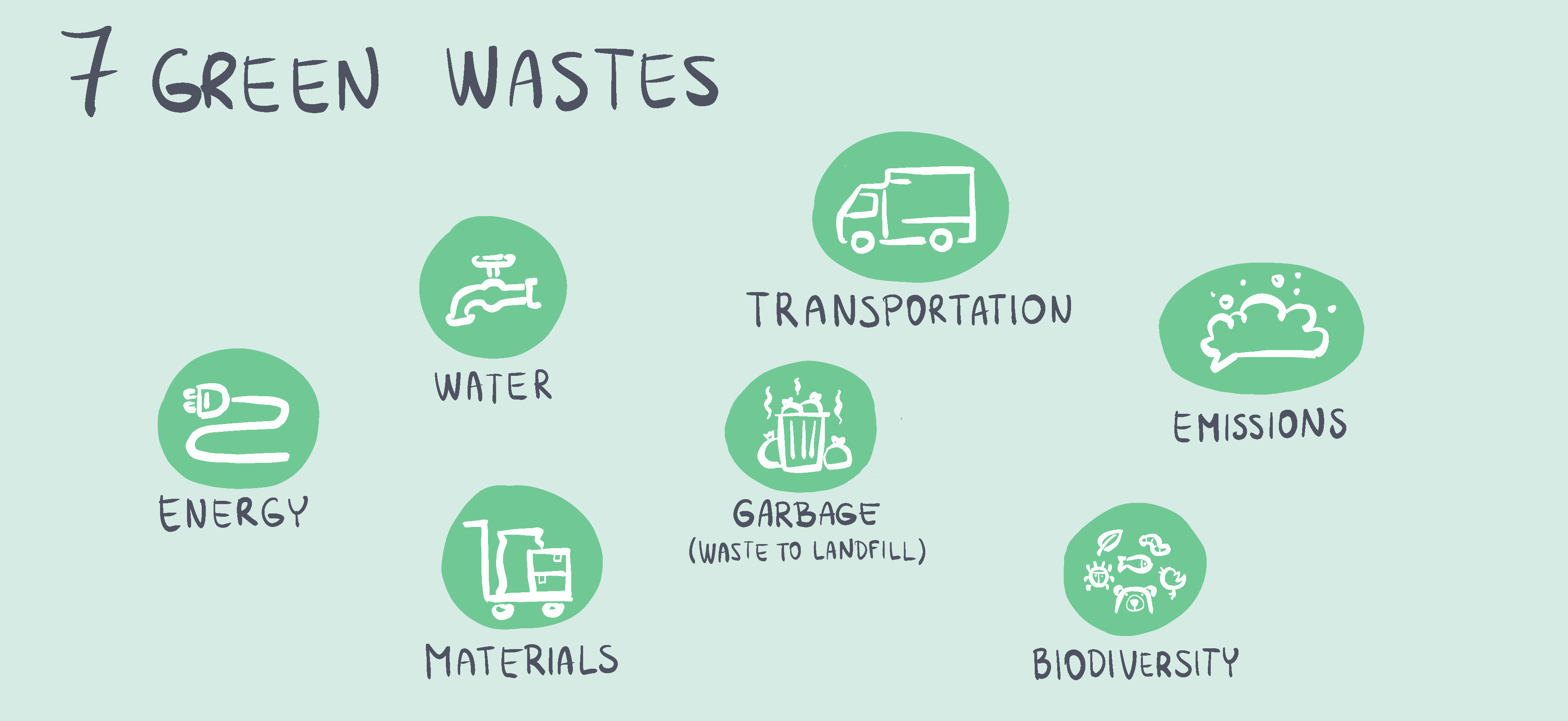
Waste Reduction and Recycling: Closing the Loop
Minimizing waste is crucial for sustainable manufacturing. This involves implementing strategies throughout the production process, from design and material selection to manufacturing and disposal. Eco-friendly factories focus on designing products for durability and recyclability, using recycled materials whenever possible, and implementing efficient waste management systems to reduce landfill waste. This includes exploring options like closed-loop systems, where waste materials are recovered and reused within the production process, creating a circular economy model.
Green Building Design and Infrastructure: Creating Efficient Spaces
The factory itself can be designed for sustainability. Green building techniques incorporate energy-efficient materials, natural lighting, and optimized ventilation systems to reduce energy consumption and improve indoor air quality. Implementing smart building management systems can further optimize energy usage and resource allocation. These strategies not only reduce the environmental impact but also contribute to a healthier and more productive work environment for employees.
Sustainable Supply Chains: Ensuring Ethical Sourcing
The sustainability of a factory extends beyond its own walls. Eco-friendly manufacturing requires collaboration with suppliers who share the same commitment to environmental responsibility. This means sourcing materials from sustainable sources, ensuring ethical labor practices throughout the supply chain, and minimizing transportation distances to reduce carbon emissions. Building strong relationships with suppliers committed to sustainability is essential for creating a truly eco-friendly production system.
Water Conservation and Treatment: Protecting Our Precious Resource
Water is a vital resource in many manufacturing processes, and its consumption can have significant environmental consequences. Eco-friendly factories implement water conservation measures such as using water-efficient technologies, recycling wastewater, and treating wastewater before discharge to protect water bodies. This not only reduces the factory’s environmental impact but also safeguards water resources for future generations.
Technological Innovations: Driving Efficiency and Sustainability
Technological advancements are playing a crucial role in driving sustainability in manufacturing. Automation, data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) can optimize production processes, reduce material waste, and improve energy efficiency. These technologies help identify areas for improvement, enabling factories to fine-tune their operations and minimize their environmental footprint. Investing in research and development of green technologies is crucial for fostering continuous improvement in sustainable manufacturing practices.
Employee Engagement and Training: Fostering a Culture of Sustainability
Creating a truly eco-friendly factory requires the engagement and commitment of the entire workforce. Employees should be trained on sustainable practices and empowered to contribute to the factory’s sustainability goals. Fostering a culture of sustainability within the organization can lead to greater innovation, improved efficiency, and a stronger sense of purpose amongst employees, creating a more positive and productive work environment.
The Economic Benefits of Going Green
While transitioning to eco-friendly manufacturing requires an upfront investment, the long-term economic benefits are significant. Reduced energy consumption, lower waste disposal costs, and improved efficiency can lead to substantial cost savings. Furthermore, the growing demand for sustainable products creates new market opportunities for eco-conscious businesses, enhancing their competitiveness and profitability. Investing in sustainability is not just an environmental imperative but a sound business strategy. Please click here to learn about sustainable manufacturing companies.
Sustainable Manufacturing A Greener Future
The Growing Urgency for Sustainable Practices
Our planet is facing unprecedented environmental challenges, and the manufacturing sector, a significant contributor to pollution and resource depletion, must take a leading role in finding solutions. The sheer scale of global production means even small improvements in efficiency and sustainability can have a massive positive impact. Ignoring this responsibility isn’t just ethically questionable; it’s also increasingly bad for business, with consumers becoming more conscious of their purchases’ environmental footprint and demanding greater transparency and accountability from companies.
Reducing Waste: A Core Principle of Sustainable Manufacturing
Minimizing waste is fundamental to sustainable manufacturing. This involves a holistic approach, encompassing the entire lifecycle of a product, from design and material sourcing to production and disposal. Strategies include implementing lean manufacturing principles to eliminate unnecessary steps and reduce material usage, embracing circular economy models that prioritize reuse and recycling, and meticulously managing waste streams to minimize landfill contributions. Innovative technologies like 3D printing also offer opportunities to create products with less waste by producing only what is needed, on demand.
Sustainable Sourcing: Choosing Eco-Friendly Materials
The materials used in manufacturing have a profound impact on the environmental cost of a product. Sustainable manufacturing necessitates a commitment to sourcing materials responsibly. This includes prioritizing recycled materials whenever possible, opting for sustainably harvested timber and other renewable resources, and sourcing materials from suppliers who adhere to stringent environmental and social standards. Transparency and traceability in supply chains are crucial to ensure accountability and prevent greenwashing.
Energy Efficiency: Powering a Greener Future
Manufacturing processes are often energy-intensive, contributing significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable manufacturing prioritizes energy efficiency through various strategies. This includes investing in energy-efficient equipment, optimizing production processes to minimize energy consumption, adopting renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, and implementing smart energy management systems. These efforts not only reduce the environmental impact but also often lead to cost savings in the long run.
Water Conservation: A Precious Resource
Water is essential for many manufacturing processes, but its overuse and contamination pose significant environmental risks. Sustainable manufacturing calls for significant water conservation efforts. This can be achieved through implementing water-efficient technologies, recycling and reusing wastewater, and adopting closed-loop systems that minimize water consumption. Regular monitoring and audits are critical to ensure efficient water management and identify areas for improvement.
Minimizing Pollution: Protecting Air and Water Quality
Manufacturing processes can release harmful pollutants into the air and water, negatively impacting human health and the environment. Sustainable manufacturing demands a commitment to minimizing pollution through various methods. This includes investing in cleaner production technologies, implementing robust pollution control systems, adhering to stringent environmental regulations, and regularly monitoring emissions to ensure compliance. Continuous improvement and innovation are essential to further reduce the environmental footprint of manufacturing activities.
Employee Wellbeing and Ethical Labor Practices
Sustainable manufacturing extends beyond environmental considerations to encompass social responsibility. Creating a safe and healthy work environment for employees, ensuring fair wages and working conditions, and promoting ethical labor practices are integral aspects of sustainable manufacturing. This involves fostering a culture of respect and inclusivity, providing opportunities for employee development, and actively addressing any human rights concerns within the supply chain.
Collaboration and Innovation: A Collective Effort
Achieving truly sustainable manufacturing requires a collective effort. Collaboration among manufacturers, suppliers, policymakers, researchers, and consumers is vital to drive innovation, share best practices, and establish industry-wide standards. Investing in research and development to explore new technologies and processes is crucial for continuous improvement and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in sustainable manufacturing. Open communication and information sharing are key to fostering a collaborative environment that promotes progress and shared responsibility.
The Economic Benefits of Sustainability
While often viewed through an environmental lens, sustainable manufacturing also offers significant economic benefits. Reduced waste, increased energy efficiency, and responsible sourcing can lead to cost savings, improved resource utilization, and enhanced brand reputation. Consumers are increasingly willing to pay more for sustainably produced goods, creating new market opportunities and driving innovation. This long-term perspective positions businesses for future success in a world increasingly focused on environmental responsibility. Click here to learn about sustainable manufacturing.

