Edge Computing Boosting Telecom Speed & Reliability
The Bottleneck of Centralized Networks
For years, the telecommunications industry relied heavily on centralized data centers. Think of it like this: all your data travels a long way – to a far-off server – before being processed and sent back. This central processing model, while functional, creates a significant bottleneck, especially as demand for high-bandwidth applications like video streaming and online gaming explodes. The longer the distance data has to travel, the greater the latency – that frustrating delay that makes your online experience sluggish. This centralized approach also creates a single point of failure; if the central data center goes down, services for potentially millions of users are impacted.
Edge Computing: Bringing Processing Closer to the User
Edge computing offers a compelling solution to these challenges. Instead of relying solely on distant data centers, edge computing pushes processing power closer to the source of the data – the user’s device or a nearby network node. Imagine mini data centers strategically placed throughout a city or region. This distributes the workload, significantly reducing the distance data needs to travel for processing. This proximity translates directly to faster speeds and lower latency, resulting in a smoother and more responsive user experience.
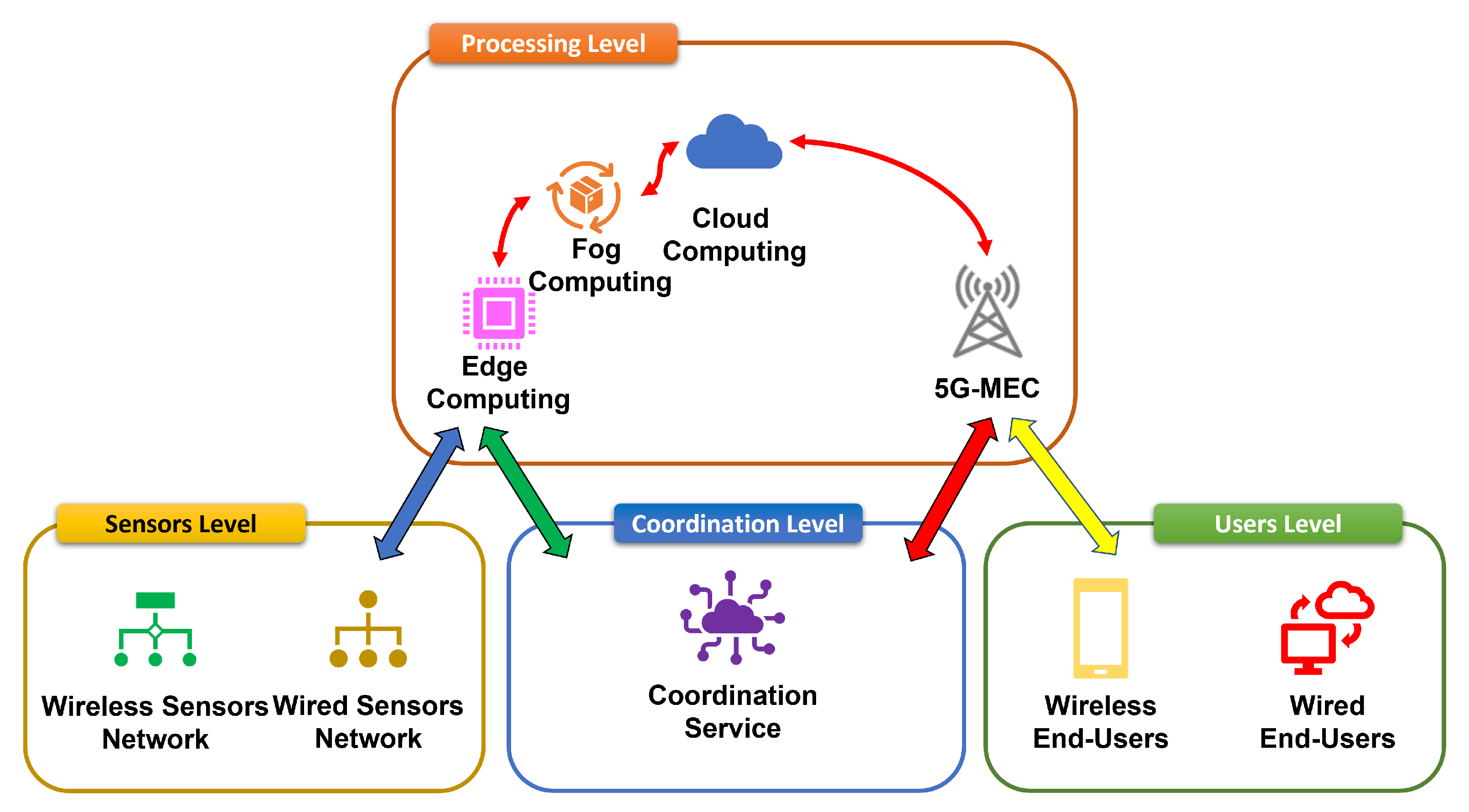
Enhanced Speed and Lower Latency: A Tangible Impact
The impact of edge computing on speed and latency is immediately noticeable. Think about streaming high-definition video. With a centralized system, even the slightest network congestion can lead to buffering and interruptions. With edge computing, however, the video stream is processed closer to your device, minimizing the impact of network congestion and leading to a far smoother viewing experience. Similarly, online gaming benefits significantly, with reduced lag and improved responsiveness that enhance the overall gameplay.
Increased Reliability and Resilience
Beyond speed improvements, edge computing enhances the reliability and resilience of telecommunications networks. By distributing processing across multiple edge locations, the system becomes less susceptible to single points of failure. If one edge node goes down, other nodes can seamlessly take over, minimizing service disruptions. This distributed architecture offers a significant advantage in terms of network robustness and uptime, ensuring a more consistent and dependable service for users.
Improved Network Capacity and Scalability
Edge computing also addresses the growing demand for network capacity. As more and more devices connect to the network – from smartphones and smartwatches to IoT sensors and autonomous vehicles – the strain on centralized data centers increases exponentially. Edge computing alleviates this pressure by distributing the processing load. This distributed approach makes it easier to scale network capacity to meet the ever-growing demands of a connected world without significant infrastructure overhauls.
Enabling New Applications and Services
The low latency and enhanced processing capabilities offered by edge computing are enabling a new wave of innovative applications and services. Real-time data analytics, augmented reality applications, and autonomous vehicle navigation are all heavily reliant on low latency communication. Edge computing makes these applications not only possible but also practical, opening up exciting new opportunities for both telecom providers and their users.
Addressing Security Concerns in a Distributed Environment
While edge computing offers many advantages, security concerns naturally arise in a distributed environment. Protecting data and ensuring the integrity of edge nodes requires a multi-layered security approach. This includes robust access control mechanisms, encryption protocols, and regular security audits. Telecom providers are investing heavily in security solutions to mitigate the risks associated with edge computing, ensuring the safe and secure handling of sensitive user data.
The Future of Telecom: A Collaborative Ecosystem
The successful implementation of edge computing in the telecom industry requires collaboration between various stakeholders. This includes telecom providers, technology vendors, and application developers. Building a robust and scalable edge computing infrastructure necessitates a coordinated effort, involving the development of common standards and interoperability protocols. As this ecosystem matures, we can expect to see even more significant advancements in the speed, reliability, and capabilities of telecommunications networks. Read also about edge computing solutions for telecom.
